Understanding Universal Connection Types: A Guide to USB, SATA, PCI, and More
USB Connection Types SATA PCI Technology Hardware Computing Universal Connectors
Understanding Universal Connection Types: A Guide to USB, SATA, PCI, and More
In the fast-evolving world of technology, universal connection types are the unsung heroes that allow our devices to communicate, transfer data, and power up. From the ubiquitous USB to the high-speed PCI, these connectors have become essential components of modern computing. In this post, we'll explore the different types of universal connections, their evolution, and their applications in everyday technology.
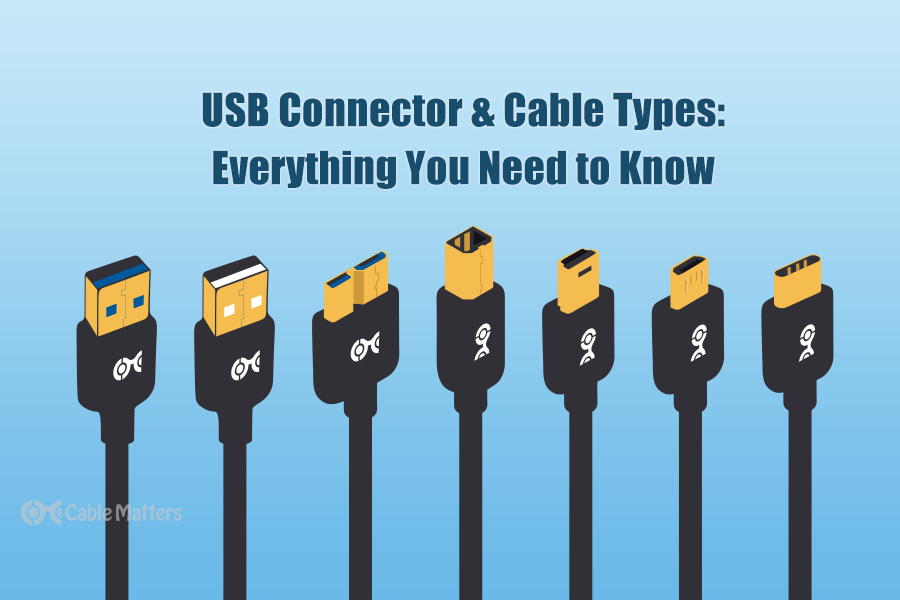
USB (Universal Serial Bus)
USB 2.0
Introduced in the year 2000, USB 2.0 became the standard for connecting a wide range of devices, such as keyboards, mice, printers, and external storage. With a maximum data transfer rate of 480 Mbps, USB 2.0 was a significant improvement over its predecessor, USB 1.1, which was limited to 12 Mbps. Despite being slower by today’s standards, USB 2.0 is still widely used for peripherals that do not require high-speed data transfer.
USB 3.0 and USB 3.1
USB 3.0, also known as SuperSpeed USB, was introduced in 2008, offering data transfer rates of up to 5 Gbps—more than ten times faster than USB 2.0. This made it ideal for high-speed storage devices like external hard drives and flash drives. USB 3.1, which arrived in 2013, further doubled the data transfer rate to 10 Gbps, making it suitable for even more demanding applications like 4K video transfers.
USB 3.2 and Beyond
USB 3.2, launched in 2017, continued the trend of increasing speed, offering up to 20 Gbps with the right hardware. It also introduced the concept of multiple lanes, allowing for even faster data transfer. The latest USB4 standard, announced in 2019, supports speeds up to 40 Gbps and is compatible with Thunderbolt 3, making it one of the fastest and most versatile connection types available today.
USB Type-B and USB Type-C
While USB Type-B is less common today, it was widely used for printers, scanners, and some external drives. However, USB Type-C, introduced in 2014, has quickly become the universal standard. With its reversible design, high power delivery, and compatibility with a wide range of protocols (including USB 3.2, Thunderbolt, and DisplayPort), USB Type-C is now the go-to connector for most modern devices.
SATA (Serial ATA)
SATA is a connection standard used primarily for connecting storage devices like hard drives, SSDs, and optical drives to a computer's motherboard. Introduced in 2003, SATA replaced the older PATA (Parallel ATA) standard, offering faster data transfer rates and more efficient cable management.
SATA Revisions
SATA has gone through several revisions, with SATA I offering 1.5 Gbps, SATA II providing 3 Gbps, and SATA III (the most common today) supporting up to 6 Gbps. Despite being surpassed in speed by newer technologies like NVMe, SATA remains a popular choice for many internal and external storage solutions due to its reliability and widespread compatibility.
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect)
PCI is a high-speed interface used to connect expansion cards, such as graphics cards, network cards, and sound cards, to a computer's motherboard. The PCI standard has evolved over the years, with PCI Express (PCIe) being the most recent and widely used version.
PCIe Versions and Lanes
PCIe is available in various versions (e.g., PCIe 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, and the latest 5.0), each offering increased data transfer speeds. PCIe also supports multiple lanes (x1, x4, x8, x16), allowing for flexible bandwidth allocation depending on the needs of the connected device. For example, a PCIe x16 slot is typically used for graphics cards, providing maximum bandwidth for demanding applications like gaming and 3D rendering.
Other Common Connection Types
Thunderbolt
Thunderbolt, developed by Intel, is a high-speed connection type that combines PCIe and DisplayPort protocols into a single interface. Thunderbolt 3, which uses the USB Type-C connector, supports data transfer rates up to 40 Gbps, making it ideal for connecting high-performance peripherals like external GPUs and 4K monitors.
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface)
HDMI is the standard connection type for transmitting high-definition video and audio between devices, such as TVs, monitors, and gaming consoles. HDMI supports various resolutions and refresh rates, including 4K and 8K, and is backward compatible with older versions of the standard.
Ethernet
Ethernet is the standard connection type for wired networking, providing reliable and fast internet connections. Ethernet cables are available in various categories (e.g., Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a), each offering different speeds and bandwidth capabilities. Ethernet remains the preferred choice for high-speed, low-latency connections, especially in professional and gaming environments.
Conclusion
Universal connection types have evolved significantly over the years, adapting to the growing demands of modern technology. From the ubiquitous USB to the high-speed PCIe, these connectors ensure that our devices can communicate, transfer data, and power up efficiently. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovations in connection types, driving the future of computing and digital connectivity.
Thank you for reading, and stay tuned for more insights and tips as we continue our tech journey together!